How to Choose a PC Power Supply
How to Choose a Power Supply for Your PC
Since the Power Supply Unit is literally the heart of your PC, considerations can sometimes go beyond mere aesthetics to attain the necessary requirements for every component to run efficiently and ensure your PC is properly built. Of course, once you’ve identified your PC build’s needs, you can start window-shopping for a PSU that aligns with the feng shui of your rig. When all intents and purposes align, the beauty and power of a perfectly-assembled machine cannot be understated.
This PC power supply guide provides the essentials of how to pick a PSU that works for your system.
How to Choose a PSU for a PC: PSU Basics
A PSU converts alternating current (AC) from the wall socket into direct current (DC) for your computer's internal components:
- Transformer: Steps the AC voltage up or down, isolates the electronic system from the AC power, and protects sensitive components from electrical fluctuations.
- Rectifier: This device converts AC power into pulsating DC power and smooths it to a steady, consistent current.
- Capacitors: Smooth out the pulsating DC power by preventing unexpected changes in input voltage. They are often used with inductors to filter out power spikes.
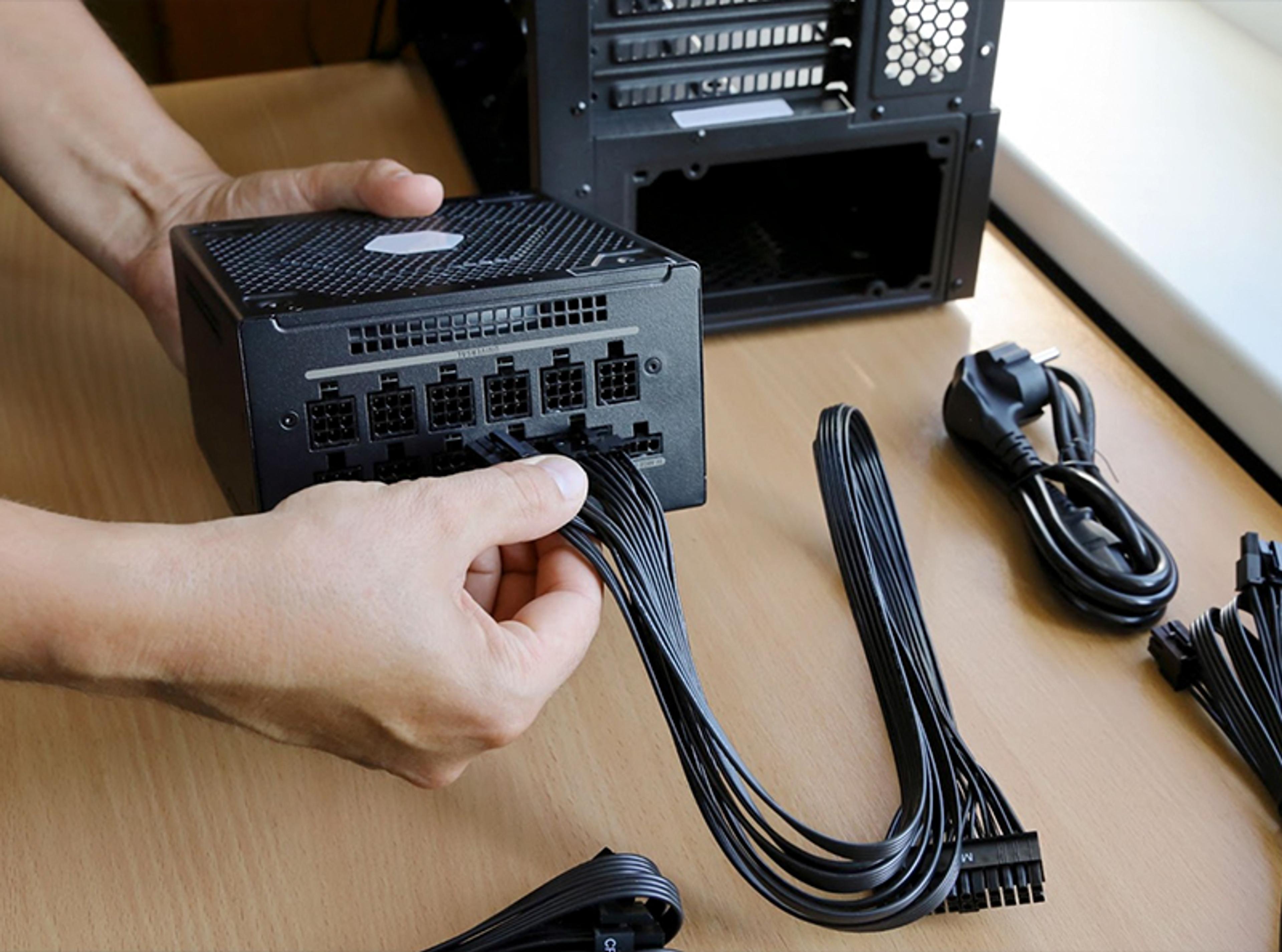
- ATX Connector: The 24-pin ATX connector supplies the correct voltage and power to the motherboard, CPU, RAM, and other components.
- Cables: The PSU’s cables connect to different computer parts, and some PSUs come with additional cables for peripherals such as graphics cards and storage devices.
Why The PSU is Important
The PSU is vital for reliable performance since computer components operate on DC power. It allows for a consistent power flow to maintain system stability and efficiency.
Many overlook the PSU despite its importance, but choosing the wrong one can have serious repercussions. Choosing a PSU that does not provide adequate or stable power can lead to voltage fluctuations and power surges, damaging critical components. These issues can cause system instability, random shutdowns, and permanent hardware failure.
What Power Supply Do I Need?
Choosing a PSU that works for your PC means accounting for each component's power consumption, including extra peripherals and cards, like sound cards or storage drives. The thermal design power (TDP) rating measures the maximum power a CPU will consume under load. For GPUs, check the manufacturer's specifications for the maximum power draw. The motherboard and RAM typically consume less energy, but still include them in your calculations.
You can use online PSU calculators to simplify this process, as you can input your components and estimate the total wattage required. Aim for a PSU that provides slightly more power than your calculated needs to ensure stability and accommodate future upgrades.
How to Choose a PSU: Features to Consider
When choosing a PSU for your PC, you need to consider wattage, efficiency, modularity, and form factors to decide based on your current and future needs.
Wattage
Wattage determines how much power your PSU can provide to your system's components. For example, a 500-watt PSU can deliver up to 500 watts of electrical power distributed across various rails for different components.
Peak and continuous wattage are two important terms to remember when choosing a PSU. Continuous wattage is the amount of power the PSU can provide continuously under normal operating conditions. Peak wattage represents the maximum power the PSU can supply for short bursts. While peak wattage shows the PSU's capacity for sudden power demands, continuous wattage is a more reliable measurement for everyday performance.
Efficiency Rating
Efficiency ratings measure how effectively a PSU converts AC power from a wall outlet into usable DC power for your components. Higher efficiency means less wasted energy and heat, which leads to better performance.
The 80 PLUS certification system rates PSUs based on efficiency at 20%, 50%, and 100% of their rated load. All PSUs with this certification guarantee at least 80% efficiency.
The certification levels are:
- 80 PLUS
- 80 PLUS Bronze
- 80 PLUS Silver
- 80 PLUS Gold
- 80 PLUS Platinum
- 80 PLUS Titanium
Choosing a PSU with a Bronze or Silver-rated PSU is sufficient for budget builds, but a Gold-rated PSU perfectly balances performance and cost for most users. Platinum and Titanium ratings are best for high-end systems and anyone wanting top-tier efficiency and minimal heat generation.
Modularity
Modularity impacts cable management, installation, and the overall aesthetics of your build. There are three types of PSU modularity:
- Non-Modular PSUs: A budget-friendly option where all cables are permanently attached to the unit, so you have cables for all connections, even if you don't need them. The extra, unused cables can clutter your PC case, affect airflow, make your build look less tidy, and lead to a more complicated installation.
- Semi-Modular PSUs: Some cables are permanently attached, usually the essential ones like the 24-pin ATX and the 8-pin CPU connectors. Other cables for GPUs and additional drives can be connected as needed. Semi-modular PSUs provide a clean while being easier to manage than fully modular units, as you can disconnect the cables to reduce clutter.
- Fully Modular PSUs: No cables are attached, so you can connect only the cables needed for your build. These modular PSUs are best for a tidy and efficient build, reducing excess clutter and improving airflow.
While non-modular PSUs are cost-effective and sufficient for many builds, investing in a modular PSU is worth it for a clean, organized build and optimal airflow.
Form Factor
The form factor determines the physical size and shape of the PSU, affecting how it fits within your case and overall system design. Below are the most common PSU form factors and how to ensure compatibility with your case.
- ATX: Designed to fit in mid-tower and full-tower cases and are suitable for standard builds.
- SFX: More compact for small form factor (SFF) builds, like mini-ITX cases, where space is limited. However, they often provide lower wattage.
- SFX-L: A variation of the SFX form factor with more depth for increased power capacity and cooling efficiency. They are best for compact builds requiring higher wattage or enhanced cooling.
- TFX: These form factors are thin and designed for slimline desktops.
Choosing a compatible PSU form factor ensures an efficient build. Always carefully check the dimensions and clearance requirements to ensure all components fit. If you plan on upgrading your components or adding new hardware, choose a PSU that offers size and power capacity flexibility.
How to Choose a PSU: Other Features to Consider
When choosing a PSU, a couple of other features can impact your system's performance and safety, including:
- Protection features such as Over-Voltage Protection (OVP), Over-Current Protection (OCP), Short-Circuit Protection (SCP), and a surge protector.
- Most users prefer a PSU with low-noise features and high efficiency. Larger fans move more air at slower speeds, while higher-efficiency units generally produce less heat, allowing them to operate at a quieter level.
How to Pick a PSU for Your Build
Choosing a PSU is crucial for your PC's stability, performance, and longevity. The best PSU for your PC build depends on your needs and the specifications, such as power usage and case size. If you want the best cases for your PC build, check out HYTE's ATX PC Cases and ITX PC Cases for a sleek and aesthetic-looking gaming PC.
Featured Posts

Black Friday Gaming Gear & PC Deals 2025
HYTE Black Friday sales are here, and we’re excited to share the amazing deals we’ll be offering this year! Our Black Friday sales event is your chance to save big on some of our most popular products. From November 20th through December 2nd, enjoy incredible discounts on PC cases and gaming accessories that bring both performance and style to your setup. If you’re looking to upgrade, now’s the perfect time to do it with HYTE.

Official HYTE x Honkai: Star Rail Firefly Collection!
The stars have aligned, and the Official HYTE x Honkai: Star Rail Firefly Collection is ready for launch.

HYTE's 4th Anniversary Sale!
We’ve come a long way, and it’s all thanks to you! To celebrate HYTE’s anniversary, we’re giving back with a limited-time Anniversary Sale from Oct. 5 to Oct. 7.

HYTE X50 & X50 Air Pre-Orders Are Now Live!
The X50 redefines typical PC cases with a unique curved design and performance-driven elements. Pre-order the X50 and X50 Air NOW!