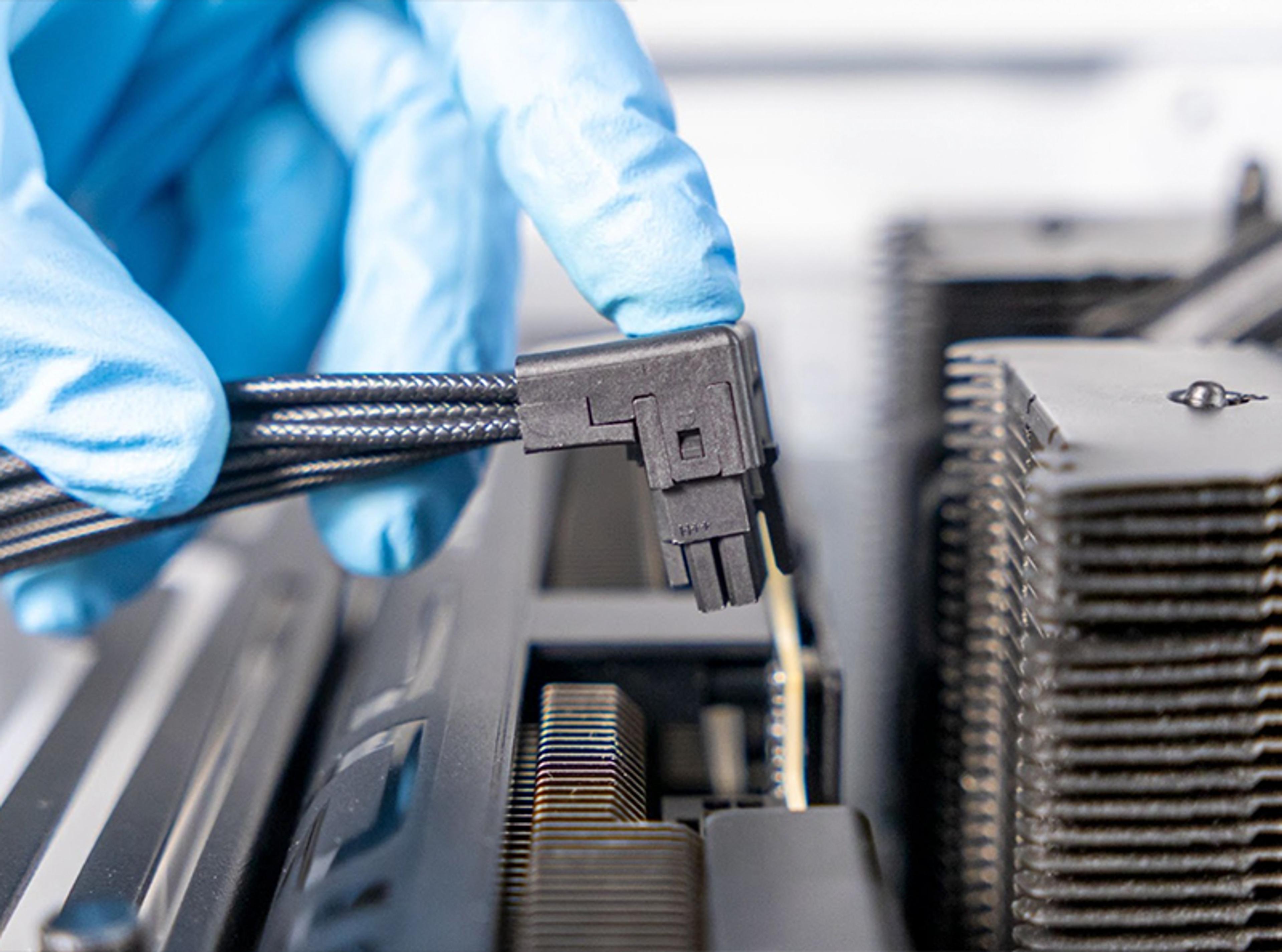
What is PCIe & How Does it Work?
What is PCIe & How Does It Work?
Speed and efficiency are paramount when it comes to anything computer-related. A crucial mechanism that helps with this is PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), which facilitates communication between all the components in a PC case and the motherboard, from powering high-end graphics cards to enabling ultra-fast NVMe SSDs.
This guide will help you understand everything you need to know about PCIe and how it works.
What is PCIe?
PCIe is a high-speed interface for data transfer between electronic components. It allows uninterrupted communication between a system's components and its motherboard. By connecting components directly to the motherboard, PCIe ensures that the computer operates efficiently and delivers the necessary performance for demanding tasks. PCIe is used on desktop and mobile computers, server systems, and even gaming consoles and set-top boxes.
One key feature of PCIe is its ability to adapt to different performance needs through lanes. These lanes are pathways for data transfer, and their number can vary depending on the speed requirements of the connected device. For example, larger lanes like PCIe x16 are ideal for high-bandwidth devices, while smaller lanes like PCIe x1 are for peripherals requiring less bandwidth.
PCIe vs. PCI
PCIe is significantly faster and more efficient than PCI due to its serial data transfer protocol, which dedicates bandwidth to each lane. Unlike PCI, which uses a parallel bus where all devices share the same bandwidth, PCIe's design eliminates bottlenecks for faster, more reliable data transfer.
Additionally, PCIe's scalability, with lane configurations like x1, x4, x8, and x16, provides flexibility for varying performance needs, unlike PCI's fixed configuration. With higher clock speeds, PCIe delivers significantly faster data transfer rates and greater versatility than the older PCI standard.
How does PCIe Work?
At its core, PCIe is a high-speed, point-to-point connection between a computer's motherboard and a PCIe-compatible device. Some common uses of PCIe include:
- Faster Storage
- Graphics Upgrades
- Multi-Monitor Setups
- Network Expansion
Unlike older shared-bus technologies, PCIe uses a dedicated communication channel for each connected device to speed up and improve data transfers. PCIe relies on differential signaling to transmit data, which means data travels over pairs of copper wires, one carrying the signal and the other its inverse. The latest PCIe generations support data rates as high as 16 GT/s, enabling ultra-fast performance for modern devices.
Lane counts, such as x1, x4, x8, or x16, categorizes PCIe slots on a motherboard. The more lanes a slot has, the higher the potential data transfer rate.
Common lane counts for PCIe include:
- x1 slots: Low-bandwidth peripherals like sound cards or network adapters.
- x4 and x8 slots: Mid-range devices such as SSDs and specific RAID controllers.
- x16 slots: High-performance graphics cards and handling large amounts of data for gaming or rendering.
By offering a scalable architecture and exceptional data transfer capabilities, PCIe has become an essential technology for powering the speed and performance of modern computing systems.
H2 Advantages of PCIe
PCIe offers numerous advantages, such as:
- Speed: Faster data transfer rates than older interfaces like USB and SATA, making it ideal for high-bandwidth gaming, video editing, and machine-learning tasks.
- Reliability: Dedicated, point-to-point architecture minimizes lag, stuttering, and bottlenecks during intense workloads, providing more consistent performance.
- Scalability: Flexible configurations with different lane sizes can accommodate various devices and performance needs.
- Versatility: Supports a range of components and can connect multiple devices simultaneously with minimal latency.
- Backward compatibility: Users can upgrade systems over time without replacing every component, as newer devices can operate in older PCIe slots at reduced speeds.
- Energy Efficiency: Incorporating power-saving features lets components run cooler, consume less energy, and maintain peak performance even under demanding workloads.
- Compatibility: PCIe is an industry-standard interface compatible with components from various manufacturers, simplifying system building and upgrades.
H2 What is PCIe 4.0?
PCIe 4.0, or PCIe Gen 4, is the fourth generation of PCIe. Its data transfer rate is 16 gigabyte transfers per second (GT/s) per lane, twice the speed of PCIe 3.0. This improved transfer rate enables faster gaming, machine learning, data processing, and cloud computing performance.
H3 When did PCIe 4.0 Come Out?
PCIe 4.0 was announced in 2017 but wasn’t widely used until 2019. When each new generation is released, the latest PCIe is twice the speed of the previous generation.
H2 How to Maximize PCIe Performance
Optimizing your system's performance begins with choosing the best motherboard with sufficient PCIe slots to accommodate your components. Properly optimizing PCIe-based components enhances performance, such as installing the GPU or NVMe SSD in the correct slot.
Focusing on lane distribution and slot bandwidth is also crucial, as these determine how data transfers between your devices and the motherboard. For example, high-performance components like GPUs typically require x16 slots for maximum bandwidth, while SSDs often utilize x4 or x2 slots. By balancing your hardware needs with the available PCIe lanes and bandwidth, you can create a system that runs efficiently and meets your specific computing requirements.
H2 Can a PCIe 4.0 Work With 3.0?
PCIe 3.0 and PCIe 4.0 are backward and forward-compatible so that users can mix and match devices across generations. The primary benefit of this cross-generation compatibility is the flexibility to upgrade systems without requiring a complete overhaul. Users can swap out components and still enhance performance while leveraging existing hardware. However, to fully utilize the speeds and features of PCIe 4.0, the device and the system must support the newer standard.
For example, a PCIe 4.0 device can function in a PCIe 3.0 slot, and a PCIe 3.0 device can work in a PCIe 4.0 slot. However, PCIe 4.0 devices used in PCIe 3.0 slots will be limited to the PCIe 3.0’s maximum speed of 8 GT/s instead of the 16 GT/s offered by PCIe 4.0 slots.
H2 Get the Most Out of Your PCIe Connections
With devices like PCIe 4.0, components communicate quickly and efficiently with each other, helping to maximize PC performance. As PCIe generations advance, the future promises even better speed and efficiency, keeping up with the demands of gaming, AI, and other resource-intensive applications.
If you’re building or upgrading your PC, understanding PCIe and choosing the right components is crucial for its performance. At HYTE, our PCIE40 Luxury PCIe 4.0 Riser Cable allows more components to connect for efficient performance. Explore the rest of our components and accessories to unlock your system’s full potential today.
Featured Posts

X50 Astral Orange Is Almost Here: Pick an Orange
The X50 Astral Orange is almost here, and we are turning up the heat in the best way we know how. It is time to celebrate the orange side of gaming.

Black Friday Gaming Gear & PC Deals 2025
HYTE Black Friday sales are here, and we’re excited to share the amazing deals we’ll be offering this year! Our Black Friday sales event is your chance to save big on some of our most popular products. From November 20th through December 2nd, enjoy incredible discounts on PC cases and gaming accessories that bring both performance and style to your setup. If you’re looking to upgrade, now’s the perfect time to do it with HYTE.

Official HYTE x Honkai: Star Rail Firefly Collection!
The stars have aligned, and the Official HYTE x Honkai: Star Rail Firefly Collection is ready for launch.

HYTE's 4th Anniversary Sale!
We’ve come a long way, and it’s all thanks to you! To celebrate HYTE’s anniversary, we’re giving back with a limited-time Anniversary Sale from Oct. 5 to Oct. 7.